If you get caught up in a radioactivity scare, make sure that your scientific advisers (and those advising lobby groups) tell you what equivalent dose (measured in millisieverts (mSv)) might be received by those exposed to the radiation.
- We on average receive a dose of 2.7mSv each year so a further dose of a few mSv is not worrying.
- Indeed, a single dose of as much as 1,000 mSv is needed to cause temporary radiation sickness such as nausea and vomiting.
- A scientist en route to Chernobyl in 2019 reported that his dosimeter recorded 1.8mSv per hour in the aeroplane ...
- ... and exceeded 12mSv per hour in only the tiny, most polluted area around the failed reactor.
And see further information about dangerous (and non-dangerous) doses below..
Some forms of radiation are dangerous, but most are not:-
- Radio waves travel through most things, including our bodies, without doing any harm. Light waves, another form of radiation, are essential to life, as is infra-red radiation which transmits heat from one place to another, and particularly from the sun to the earth.
- The air that we breathe is radioactive. This is because cosmic rays entering the atmosphere create carbon dioxide containing carbon 14, a radioactive form of carbon. This slowly turns into normal non-radioactive carbon But this happens so slowly that every gram of natural carbon (e.g. in our bodies, in the atmosphere (as Carbon Dioxide) or in plants) typically emits 15 radioactive particles every minute. This gradual reduction in radioactivity provides a way of establishing the age of very old organic material:- "carbon dating".
Radiation and radioactivity are nevertheless very scary. We have a choice about whether to accept the (much higher) risks associated with, for instance, smoking and drinking. But the risks from such things as radioactive spillages are imposed on us without our agreement. Even worse, we cannot detect radioactivity, and it poses threats to unborn generations. The public therefore understandably expect the Government to take every possible measure to protect it from this danger.
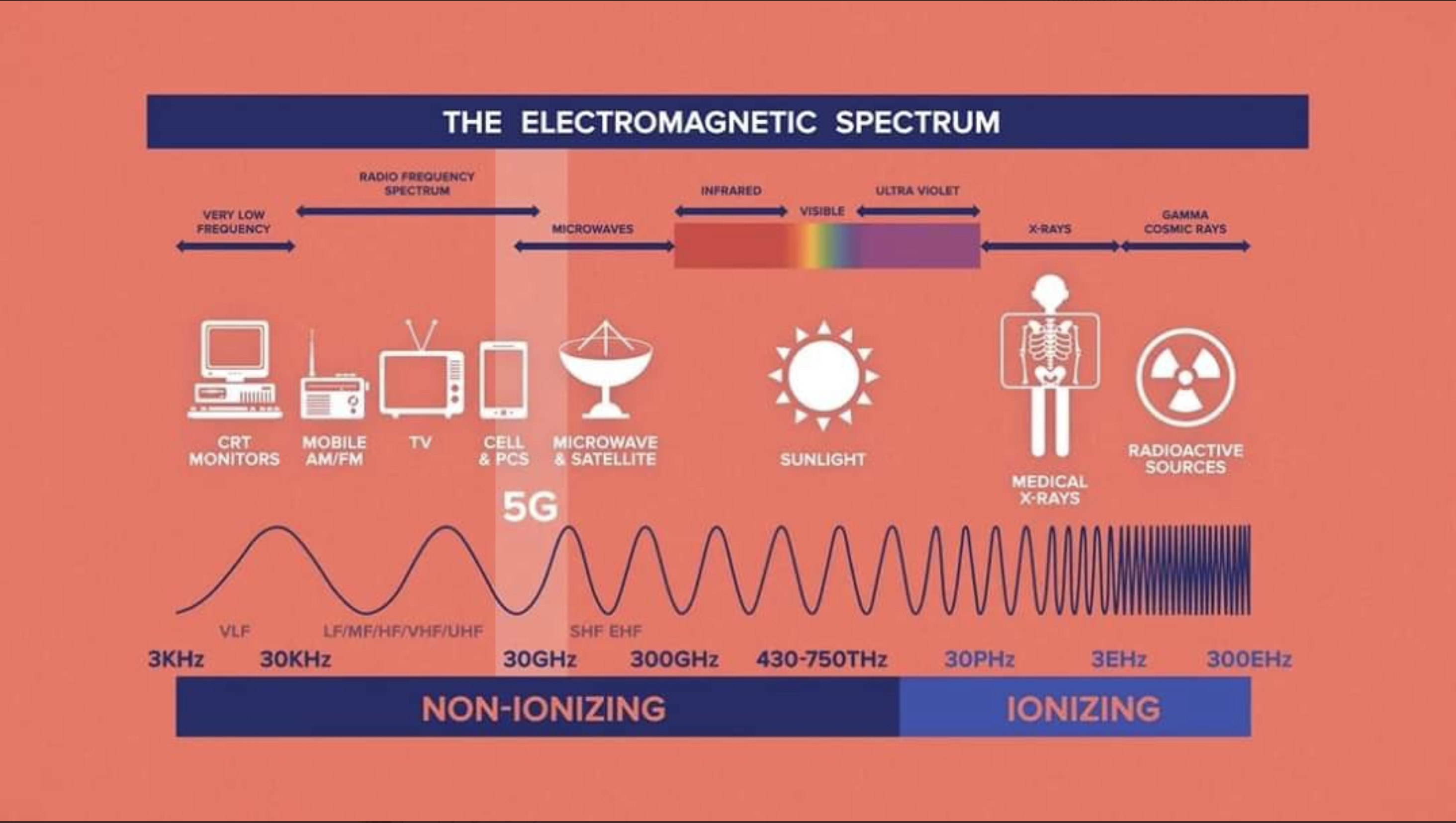
There is a radiation spectrum, ranging from very energetic and dangerous radiation through to very low energy and very safe radiation. The following are the three principal types of radiation within this spectrum, in order of decreasing energy - and so starting from the right in the above chart,
1. Ionising Radiation The most energetic radiation is very dangerous because it can ionise material in the body. Most ionisations are harmless, but there is a small chance that ionisation of DNA can cause cancer. The main components of this part of the spectrum are:
- Bits of atoms, emitted when radioactive material breaks up:- Alpha particles, Beta particles (electrons) and Neutrons.
- Next come Gamma rays
- and then X rays
2. Ultra-violet radiation comes next. These rays are less dangerous but can still cause skin cancer.
3. Visible light and radio waves make up the low energy end of the radiation spectrum. The main components, in order of decreasing energy, are:
- Visible light, ranging from Violet through to the least energetic red light
- Infra-red
- Microwaves
- UHF radio transmissions
- VHF radio transmissions
- TV transmissions
- Short wave radio
- Medium wave radio
- Long wave radio
- Very low frequency magnetic fields
Let's now look at the risk that each of the above three categories of radiation might cause cancer.
1. Radioactivity Luckily, our natural environment contains very little of the most energetic ionising radiation, otherwise known as radioactivity. But great confusion is caused by the fact that our exposure to this radiation can be measured in several ways.
- The number of particles emitted by radioactive material depends upon the material's half-life, i.e. the time that it takes for one half of each unit of material to transform into another material.
- But, if we are handling radioactive material, we are usually more interested in the number of emissions that it creates every second. Even tiny amounts of radioactive substance generate huge numbers of emissions which are measured in becquerels. The shorter the half-life, and the heavier the material, the greater the number of becquerels. But these large numbers do not really reflect the risk to humans.
- We are much more interested, of course, in the amount of energy that is absorbed by the body when it is hit by radioactivity. This is measured in grays. For instance, a heavy alpha particle delivers much more energy (that is many more grays) than a lighter beta particle.
- And we are even more interested in the damage that is done by the radioactivity, for again a heavier particle, such as an alpha particle, will leave all its energy in one place, causing maximum damage. The damage that is done is called the "equivalent dose" and is measured in sieverts. As most of us are subject to very little radioactivity in our normal lives, our personal doses are usually measured in one thousandths of a sievert or millisieverts (mSv).
- An average person in the UK receives a dose of around 2.7mSv each year - a bit more in some areas, a bit less in others. This is about 200mSv, over a lifetime.
- 1.4 of this 2.7 comes from the naturally occurring gas radon.
- Another 0.9 comes from other natural sources, including 0.3-0.4 from cosmic rays, and
- 0.4 comes from medical X rays etc. - but note that a single CT scan typically delivers 15mSv.
- Only 0.03mSv comes from industry, including radioactive discharges from power stations etc and fallout from e.g. Chernobyl.
- But some of us are subject to much higher doses.:-
- Radon gas escaping from the ground in Cornwall means that the average Cornish person receives c.8 mSv a year.
- Ramsar in Iran gives c.240 mSv a year for similar reasons.
- Some medical procedures (such as CT scans) can give doses of over 10 mSv.
- And every 20 hours in a jet plane adds 0.1mSv to our total because of increased exposure to cosmic rays.
- The legal limit for exposure for someone working with radiation in industry is 20 mSv/year.
- Almost all organic material contains radioactive Potassium 40. The human body delivers itself a dose of 0.2 mSv a year, and a single banana is said to deliver a dose of 0.0001mSV - so that a banana a day would deliver approaching 0.04 mSv a year - although much of the Potassium is subsequently excreted so the actual dose would be much lower.
Another way of looking at similar risks is compare them with day to day exposure. By this measure, for instance, a chest X-ray is 2.4 days, and an abdominal CT scan is 2.7 years, worth of natural background radiation.
 Finally, what about the risk of getting cancer? This is thought to be about .005% per millisievert over a lifetime. The average person in the UK receives a dose of 200mSv over a lifetime. The chances of this causing cancer are therefore 0.005% of 200 which is 1%. In other words, 1% of us will die from cancers caused by natural radioactivity. In contrast, a huge proportion of us die from cancers caused by other factors, including smoking. And a single dose of as much as 1,000 mSv is needed to cause temporary radiation sickness such as nausea and vomiting.
Finally, what about the risk of getting cancer? This is thought to be about .005% per millisievert over a lifetime. The average person in the UK receives a dose of 200mSv over a lifetime. The chances of this causing cancer are therefore 0.005% of 200 which is 1%. In other words, 1% of us will die from cancers caused by natural radioactivity. In contrast, a huge proportion of us die from cancers caused by other factors, including smoking. And a single dose of as much as 1,000 mSv is needed to cause temporary radiation sickness such as nausea and vomiting.
Therefore, if you are asked to give advice about the effect of e.g. a radioactive spillage, you should do your best to ensure that scientists tell you what equivalent dose might be received by those exposed to the radioactivity. They might well need to make a number of assumptions in calculating the dose(s), and these should be made explicit. But once you have a possible figure, you can compare it with the average annual dose and decide how to react. Clearly, a one-off dose of less than 3mSv per person need not cause huge concern. For comparison, a spinal X-ray delivers roughly 1mSv of radiation; and a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis delivers an effective dose of 15mSv. And it is hard to understand why the HSE once prosecuted the Natural History Museum for accidentally displaying some rocks which exposed visitors to 0.044mSv per hour.
Nuclear power stations generate heat (and hence steam and hence electric power) because they allow radioactivity (produced by Uranium or Plutonium) to interact with further Uranium or Plutonium and so generate both heat and more radioactivity. But once the control rods are deployed to stop such reactions - as happened immediately in Fukoshima in 2011 - then the radioactivity of the remaining Uranium or Plutonium dies away quite quickly - by about 99.9% over a week. Therefore, although very high levels were briefly registered within the Japanese plant boundary, the level was reported to be only 10 millisieverts per hour or lower for most of the period since the crisis began.
But do bear in mind that almost all predictions about the effect of radiation on the body are based on a model (the ICRP model) which was developed by using the observed cancer rates in the survivors of atomic bombs exploded over Japan during the Second World War. These were high dose, high dose-rate exposures to external radiation. These risks are extrapolated, in the ICRP model, to lower doses, lower dose-rates and internal radiation. This is called the linear, no threshold theory. Some scientists believe that these extrapolations are, and therefore the model itself is, seriously flawed. But there is no agreement about the consequence of these flaws. Some argue that we should be very concerned about the damage that might be done by substances such as depleted uranium dust which might have found its way into the lungs of soldiers and others as a result of military operations. (See a a separate note on this subject). On the other hand, there is some evidence that cellular repair mechanisms can compensate for lower doses of exposure. This may be the reason why a predicted spike in leukemia cases in people exposed to Chernobyl fallout has not been detected.
(The only proven deaths resulting from Chernobyl are therefore the c.50 that died at, or soon after, the time of the explosion, plus a dozen or so Belarus children who subsequently died of thyroid cancer, though many thousands suffered from that disease. The radiation plume that circled the Earth undoubtedly caused other deaths, but their random nature, and low rate compared with cancers caused by background radiation etc., mean that no sensible estimate can be made.)
2. Ultraviolet light Although it is non-ionising, ultraviolet light is still energetic enough to cause cancer. None of us can totally avoid UV radiation, of course, but we should try to avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight, especially if we have fair skin. A failure to avoid these precautions, together with the depletion of the ozone layer, which lets through more of the high energy UV radiation, has led to a doubling in the incidence of skin cancer in the UK, to about 5000 cases a year.
3. Visible radiation, microwaves, radio waves and electro-magnetic radiation It can be seen from the position of this radiation, in the lower part of the above spectrum, that it is very unlikely that it could be doing us any damage. In particular, there is no evidence that these waves, and in particular microwaves, could cause cancer (e.g. when using a mobile phone).
 There nevertheless remain frequent stories about the health risks associated with mobile phone masts. Click on this thumbnail to have these concerns put in perspective.
There nevertheless remain frequent stories about the health risks associated with mobile phone masts. Click on this thumbnail to have these concerns put in perspective.
The most powerful microwave photon has less than 1/1,400 of the energy of the least powerful visible photon. So - although you wouldn't want to stand for long in front of a powerful microwave transmitter - any more than you should lie for long periods on a sun-bed or in full summertime sunshine - it is inconceivable that the microwaves in, for instance, a mobile phone could do any harm at all. Indeed, we have decades of studies on exposure to radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation and there has been no correlation with the frequency of brain cancers.
There is also some concern about the effect of magnetic fields found in some houses and near electricity pylons. A March 2001 report by (what is now) the Radiation Protection Division of the Health Protection Agency (see below) found a weak but statistically valid link between such exposure and childhood leukemia. At most, the fields might be causing 2 cases of leukemia each year, out of a UK total of 500. But it is not clear how these very low energy waves could be causing cancer. It might well be that the apparent link was caused by the design of the research, or the lifestyles or other characteristics of the families that are exposed to this radiation, rather than being caused by the magnetic fields themselves. The report certainly did not merit the Evening Standard's headline:- 55,000 children are 'at risk from power radiation'.
For Further Information, start with the clear and authoritative web site of the Radiation Protection Division of the Health Protection Agency.
And see my separate note on depleted uranium for a review of the handling of one particular radiation scare in early 2001.